Molecular hydrogen attenuates gefitinib-induced exacerbation of naphthalene-evoked acute lung injury thro…
Kuwahara, Naomi et al. (2019),
Laboratory Investigation,
vol. 99,
793-806
Kuwahara, Naomi, Kajimoto, Yusuke, Suzuki, Tetsuya, Ohsawa, Ikuroh, Hamanoue, Makoto, Ohsiro, Jumi, Shimizu, Akira, Terasaki, Mika, Iketani, Masumi, Kawaguchi, Hideo, Takahashi, Mayumi, Terasaki, Yasuhiro, Tonaki, Kozue, Hattori, Seisuke (2019),
Laboratory Investigation,
vol.
99,
793-806
Although inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated cell signaling by the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib is highly effective against advanced non-small cell lung cancer, this drug might promote severe acute interstitial pneumonia. We previously reported that molecular hydrogen (H2) acts as a therapeutic and preventive anti-oxidant. Here, we show that treatment with H2 effectively protects the lungs of mice from severe damage caused by oral administration of gefitinib after intraperitoneal injection of naphthalene, the toxicity of which is related to oxidative stress. Drinking H2−rich water ad libitum mitigated naphthalene/gefitinib-induced weight loss and significantly improved survival, which was associated with a decrease in lung inflammation and inflammatory cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Naphthalene decreased glutathione in the lung, increased malondialdehyde in the plasma, and increased 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal production in airway cells, all of which were mitigated by H2-rich water, indicating that the H2-rich water reverses cellular damage to the bronchial wall caused by oxidative stress. Finally, treatment with H2 did not interfere with the anti-tumor effects of gefitinib on a lung cancer cell line in vitro or on tumor-bearing mice in vivo. These results indicate that H2-rich water has the potential to improve quality of life during gefitinib therapy by mitigating lung injury without impairing anti-tumor activity.
10.1038/s41374-019-0187-z
Hydrogen gas distribution in organs after inhalation: Real-time monitoring of tissue hydrogen concentration in rat
Yamamoto, Ryo et al. (2019),
Scientific Reports,
vol. 9,
1255
Yamamoto, Ryo, Homma, Koichiro, Suzuki, Sayuri, Sano, Motoaki, Sasaki, Junichi (2019),
Scientific Reports,
vol.
9,
1255
Hydrogen has therapeutic and preventive effects against various diseases. Although animal and clinical studies have reported promising results, hydrogen distribution in organs after administration remains unclear. Herein, the sequential changes in hydrogen concentration in tissues over time were monitored using a highly sensitive glass microsensor and continuous inhalation of 3% hydrogen gas. The hydrogen concentration was measured in the brain, liver, kidney, mesentery fat and thigh muscle of rats. The maximum concentration, time to saturation, and other measurements representing the dynamics of distribution were obtained from the concentration curves, and the results obtained for different organs were compared. The time to saturation was significantly longer (20.2 vs 6.3–9.4 min. P = 0.004 in all cases) and increased more gradually in muscle than in the other organs. The maximum concentration was the highest in liver and the lowest in the kidney (29.0 ± 2.6 vs 18.0 ± 2.2 μmol/L; P = 0.03 in all cases). The concentration varied significantly depending on the organ (P = 0.03). These results provide the fundamentals for elucidating the mechanisms underlying the in vivo favourable effects of hydrogen gas in mammalian systems.
10.1038/s41598-018-38180-4
Administration of hydrogen-rich water prevents vascular aging of the aorta in LDL receptor-deficient mice
Sakane, Iwao et al. (2018),
Scientific Reports,
vol. 8,
1-11
Sakane, Iwao, Takahashi, Mayumi, Iketani, Masumi, Komatsu, Masaki, Sekimoto, Kanako, Ohsawa, Ikuroh, Takahashi, Hiroshi, Kawaguchi, Hideo, Ohtani-Kaneko, Ritsuko, Igarashi, Tsutomu (2018),
Scientific Reports,
vol.
8,
1-11
The main cause of arteriosclerosis is atherosclerosis in the aorta. Atherosclerosis is recognized as a chronic inflammatory condition that begins with the dysfunction or activation of arterial endothelium. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and especially its oxidized form play a key role in endothelial dysfunction and atherogenesis. Recent studies showed that senescent cells are involved in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, and eliminating senescent cells suppresses the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. We previously reported that molecular hydrogen-rich water (HW) has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in numerous diseases. Here, we used LDL receptor-deficient mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 13 weeks as a model for atherosclerosis and evaluated the effects of continuous administration of HW. The numbers of endothelial cells in the atheroma expressing the senescence factors p16INK4a and p21 decreased in HFD-fed mice given HW compared with HFD-fed mice given control water. Furthermore, macrophage infiltration and Tnfα expression in the atheroma were also suppressed. These results suggest that vascular aging can be suppressed by HW.
10.1038/s41598-018-35239-0
Image-Guided Hydrogen Gas Delivery for Protection from Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Microbubbles
He, Yingjuan et al. (2017),
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,
vol. 9,
21190-21199
He, Yingjuan, Zhang, Bo, Chen, Yihan, Jin, Qiaofeng, Wu, Junru, Yan, Fei, Zheng, Hairong (2017),
ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces,
vol.
9,
21190-21199
Cardiomyocyte death induced by ischemia-reperfusion is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Hydrogen (H2), as an antioxidant, has been shown to have great potential in preventive and therapeutic applications against lethal injury that occurs from ischemia-reperfusion. However, H2 is sparingly soluble in water, resulting in its poor bioavailability in blood and damaged tissues. Here, we have developed an ultrasound-visible H2 delivery system by loading H2 inside microbubbles (H2-MBs) to prevent myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Using this system, the concentration of H2 in unit volume can be greatly improved under normal temperature and pressure conditions. H2-MBs can be visually tracked with ultrasound imaging systems and can effectively release their therapeutic gas. In vivo systemic delivery of H2-MBs in myocardial ischemic rats at the start of reperfusion resulted in a significant reduction of infarct size and pathological remodeling. Further analysis showed that this approach markedly inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis and reduced myocardial inflammation and oxidant damage in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion rats. These results indicate that H2-MBs are a promising visual delivery system for H2-based therapeutic applications.
10.1021/acsami.7b05346
Hydrogen therapy attenuates irradiation-induced lung damage by reducing oxidative stress
Terasaki, Yasuhiro et al. (2011),
American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology,
vol. 301,
L415-L426
Terasaki, Yasuhiro, Ohsawa, Ikuroh, Terasaki, Mika, Takahashi, Mikiko, Kunugi, Shinobu, Dedong, Kang, Urushiyama, Hirokazu, Amenomori, Shunsuke, Kaneko-Togashi, Mayuko, Kuwahara, Naomi, Ishikawa, Arimi, Kamimura, Naomi, Ohta, Shigeo, Fukuda, Yuh (2011),
American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology,
vol.
301,
L415-L426
Molecular hydrogen (H 2) is an efficient antioxidant that diffuses rapidly across cell membranes, reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals and peroxynitrite, and suppresses oxidative stressinduced injury in several organs. ROS have been implicated in radiation-induced damage to lungs. Because prompt elimination of irradiation-induced ROS should protect lung tissue from damaging effects of irradiation, we investigated the possibility that H 2 could serve as a radioprotector in the lung. Cells of the human lung epithelial cell line A549 received 10 Gy irradiation with or without H 2 treatment via H 2-rich PBS or medium. We studied the possible radioprotective effects of H 2 by analyzing ROS and cell damage. Also, C57BL/6J female mice received 15 Gy irradiation to the thorax. Treatment groups inhaled 3% H 2 gas and drank H 2-enriched water. We evaluated acute and late-irradiation lung damage after H 2 treatment. H 2 reduced the amount of irradiation-induced ROS in A549 cells, as shown by electron spin resonance and fluorescent indicator signals. H 2 also reduced cell damage, measured as levels of oxidative stress and apoptotic markers, and improved cell viability. Within 1 wk after whole thorax irradiation, immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting showed that H 2 treatment reduced oxidative stress and apoptosis, measures of acute damage, in the lungs of mice. At 5 mo after irradiation, chest computed tomography, Ashcroft scores, and type III collagen deposition demonstrated that H 2 treatment reduced lung fibrosis (late damage). This study thus demonstrated that H 2 treatment is valuable for protection against irradiation lung damage with no known toxicity. © 2011 the American Physiological Society.
10.1152/ajplung.00008.2011
Molecular hydrogen improves obesity and diabetes by inducing hepatic FGF21 and stimulating energy metabol…
Kamimura, Naomi et al. (2011),
Obesity,
vol. 19,
1396-1403
Kamimura, Naomi, Nishimaki, Kiyomi, Ohsawa, Ikuroh, Ohta, Shigeo (2011),
Obesity,
vol.
19,
1396-1403
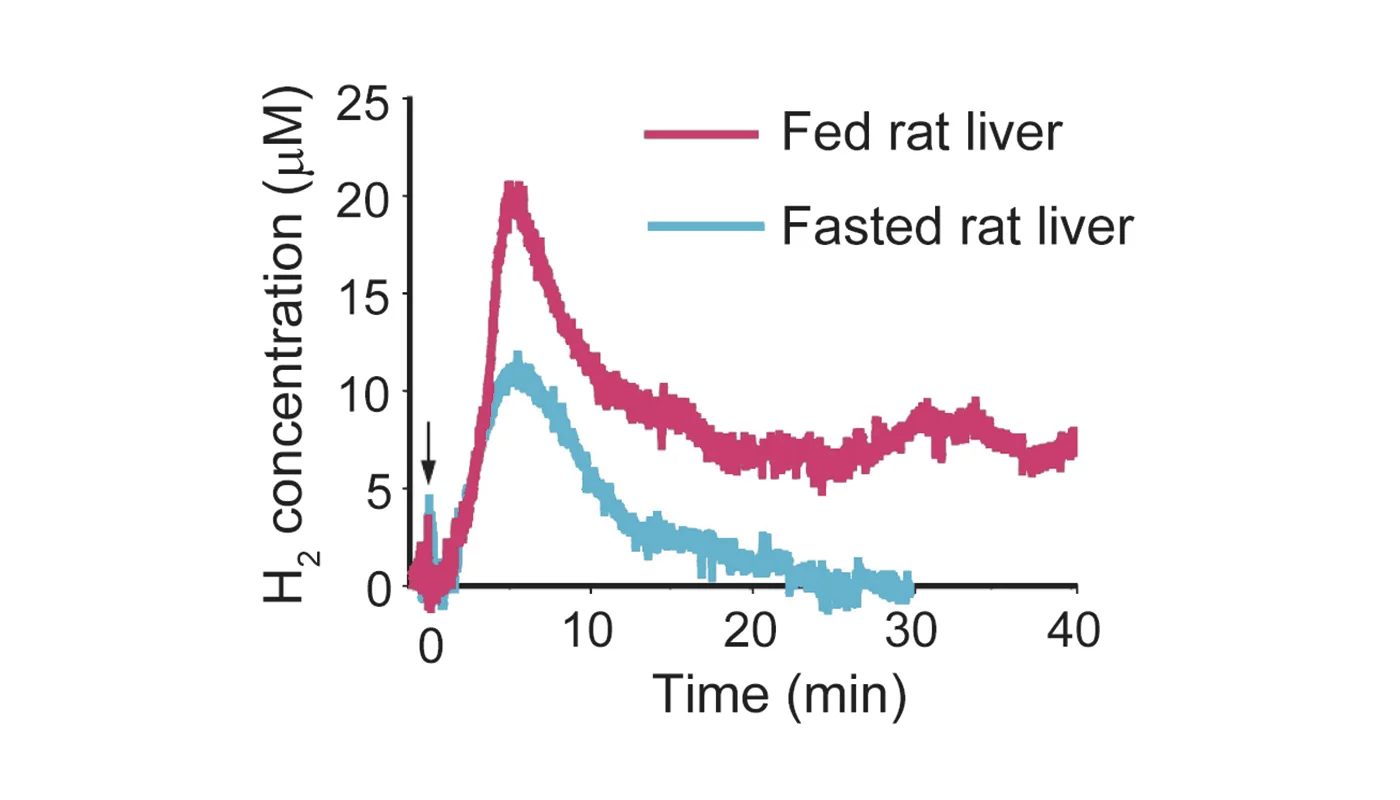
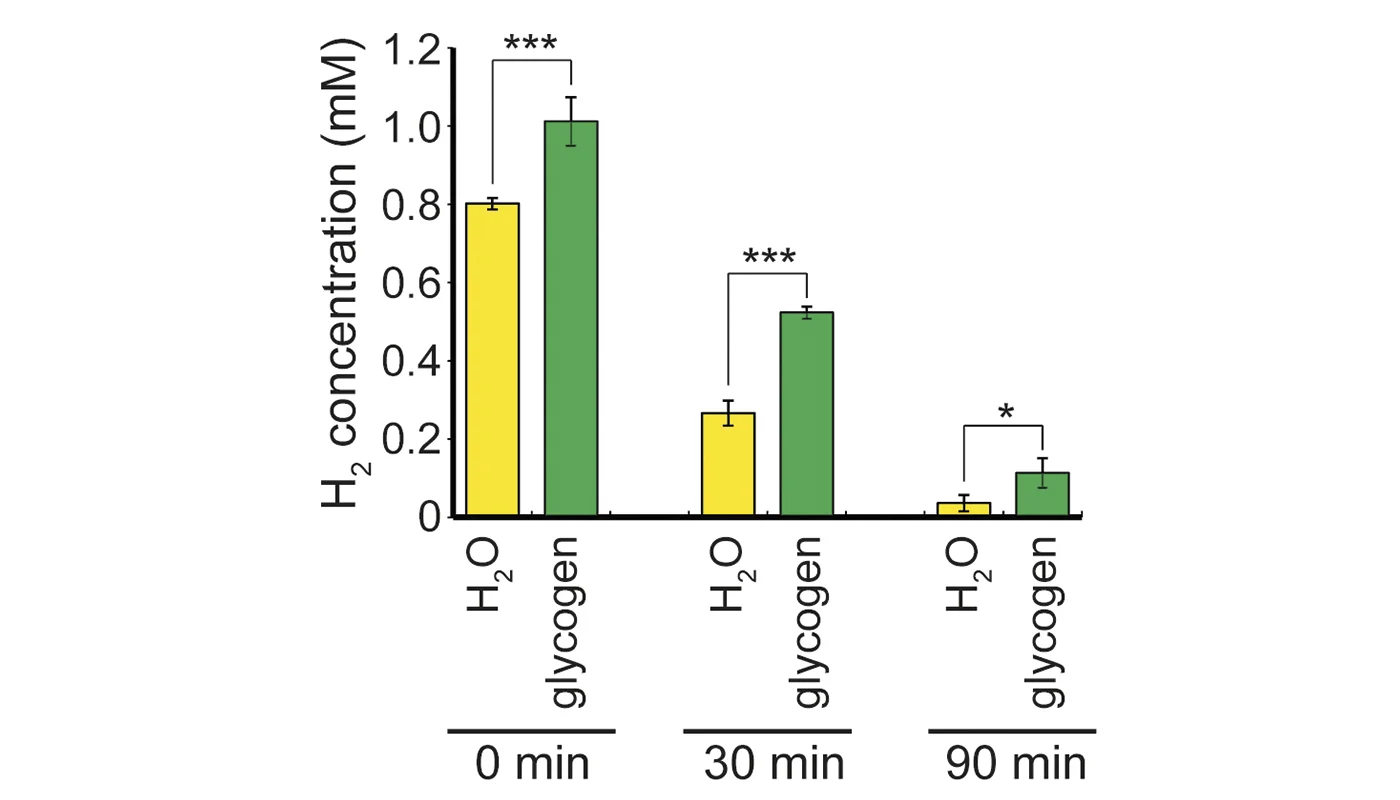
Recent extensive studies have revealed that molecular hydrogen (H 2) has great potential for improving oxidative stress-related diseases by inhaling H2 gas, injecting saline with dissolved H 2, or drinking water with dissolved H2 (H 2-water); however, little is known about the dynamic movement of H2 in a body. First, we show that hepatic glycogen accumulates H 2 after oral administration of H2-water, explaining why consumption of even a small amount of H2 over a short span time efficiently improves various disease models. This finding was supported by an in vitro experiment in which glycogen solution maintained H2. Next, we examined the benefit of ad libitum drinking H2-water to type 2 diabetes using db/db obesity model mice lacking the functional leptin receptor. Drinking H2-water reduced hepatic oxidative stress, and significantly alleviated fatty liver in db/db mice as well as high fat-diet-induced fatty liver in wild-type mice. Long-term drinking H2-water significantly controlled fat and body weights, despite no increase in consumption of diet and water. Moreover, drinking H2-water decreased levels of plasma glucose, insulin, and triglyceride, the effect of which on hyperglycemia was similar to diet restriction. To examine how drinking H2-water improves obesity and metabolic parameters at the molecular level, we examined gene-expression profiles, and found enhanced expression of a hepatic hormone, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which functions to enhance fatty acid and glucose expenditure. Indeed, H2 stimulated energy metabolism as measured by oxygen consumption. The present results suggest the potential benefit of H2 in improving obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. © 2011 The Obesity Society.
10.1038/oby.2011.6
The protective role of hydrogen-rich saline in experimental liver injury in mice
Han, Yong, Sun et al. (2011),
Journal of Hepatology,
vol. 54,
471-480
Han, Yong, Sun, L., Chen, W., Zhou, L., Hu, L., Li, Q., Tu, Y., Chang, Q., Liu, X., Sun, M., Wu, Sun, Hanyong, Chen, Lei, Zhou, Weiping, Hu, Liang, Li, Liang, Tu, Qianqian, Chang, Yanxin, Liu, Qu, Sun, Xuejun, Wu, Mengchao, Wang, Hongyang (2011),
Journal of Hepatology,
vol.
54,
471-480
Background & Aims: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are considered to play a prominent causative role in the development of various hepatic disorders. Antioxidants have been effectively demonstrated to protect against hepatic damage. Hydrogen (H 2), a new antioxidant, was reported to selectively reduce the strongest oxidants, such as hydroxyl radicals (OH) and peroxynitrite (ONOO -), without disturbing metabolic oxidation-reduction reactions or disrupting ROS involved in cell signaling. In place of H 2 gas, hydrogen-rich saline (HS) may be more suitable for clinical application. We herein aim to verify its protective effects in experimental models of liver injury. Methods: H 2 concentration in vivo was detected by hydrogen microelectrode for the first time. Liver damage, ROS accumulation, cytokine levels, and apoptotic protein expression were, respectively, evaluated after GalN/LPS, CCl 4, and DEN challenge. Simultaneously, CCl 4-induced hepatic cirrhosis and DEN-induced hepatocyte proliferation were measured. Results: HS significantly increased hydrogen concentration in liver and kidney tissues. As a result, acute liver injury, hepatic cirrhosis, and hepatocyte proliferation were reduced through the quenching of detrimental ROS. Activity of pro-apoptotic players, such as JNK and caspase-3, were also inhibited. Conclusions: HS could protect against liver injury and also inhibit the processes leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocyte compensatory proliferation. © 2010 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.011